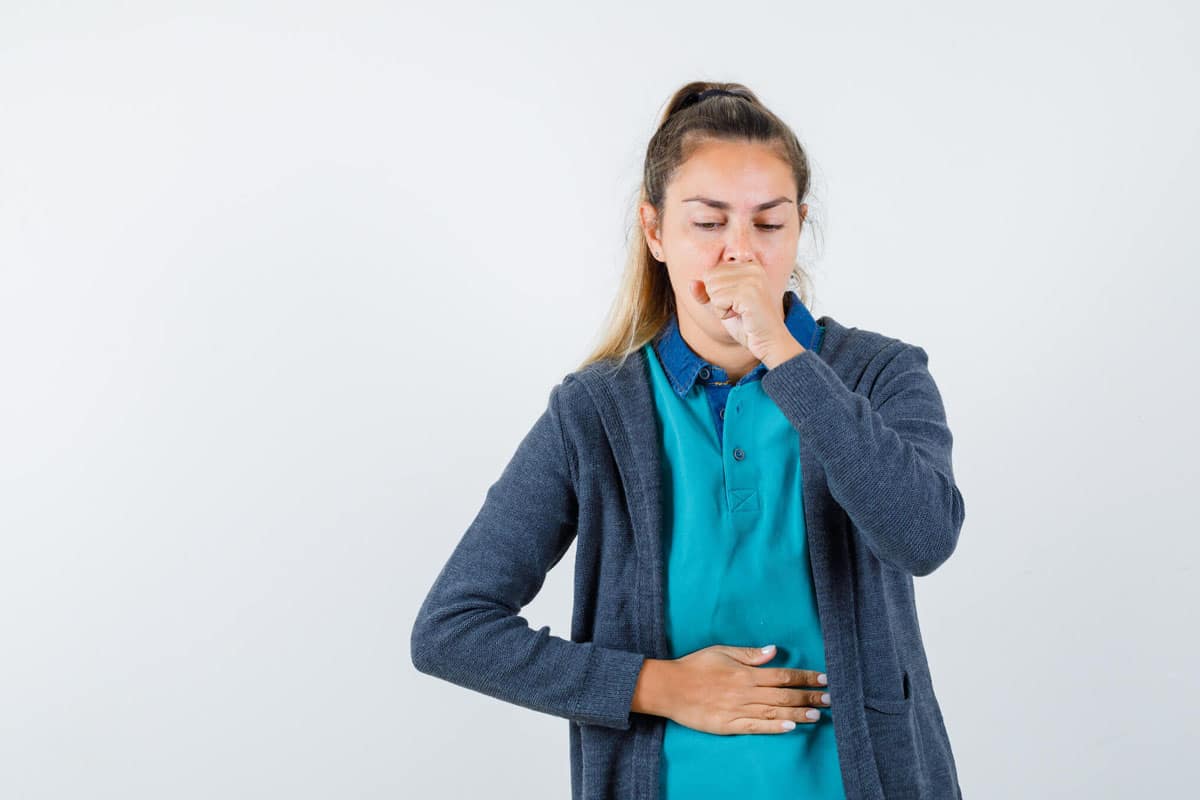
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, known as GERD, is a condition in which stomach acids flow back into the esophagus, causing symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. If not properly treated, GERD can lead to serious complications that affect the quality of life. The complications of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) can vary in frequency and severity depending on various factors, including the severity and duration of acid reflux, as well as the effectiveness of treatment.
While an evaluation by a specialist is necessary to detect potential GERD complications, paying attention to certain symptoms or signs can be helpful. Therefore, if you experience chest pain, difficulty swallowing, frequent regurgitation of stomach acid, persistent cough that does not improve with conventional treatments, hoarseness, chronic irritation of the vocal cords and throat, and unexplained weight loss, it is important to consult your doctor.
Common Complications of GERD
Some people may experience more serious and more frequent complications than others. Among the potential complications of GERD are the following:
Erosive Esophagitis
Erosive esophagitis is an inflammation of the lining of the esophagus caused by stomach acid. It can cause chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and other discomforting symptoms.
Esophageal Stricture
Esophageal stricture occurs when the esophagus narrows due to scarring caused by stomach acid damage. This can make it difficult for food and liquids to pass through.
Esophageal Ulcers
Esophageal ulcers can cause bleeding, pain, and serious complications if not promptly treated.
Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is a serious complication of GERD in which the lining of the esophagus changes due to repeated exposure to stomach acid. This increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
Asthma and Respiratory Problems
Acid reflux can irritate the airways and trigger or worsen symptoms of asthma and other respiratory conditions.
Aspiration Pneumonia
When stomach contents flow back into the esophagus and reach the lungs, it can cause aspiration pneumonia, a serious lung infection.
Eroded Teeth
Stomach acid that flows back into the esophagus can reach the mouth, which can erode dental enamel and increase the risk of cavities and other dental problems.
You may also be interested in: Explore the Best Treatment Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux
Management of GERD and Prevention of Complications
It is essential to effectively treat GERD to prevent the onset of serious complications. Treatments may include lifestyle changes, medications to reduce stomach acid production, and in some cases, surgery to correct structural problems.
Healthy Diet: It is important to recognize and avoid foods that often trigger acid reflux, such as spicy, fatty, and citrus foods.
Weight Control: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the stomach and improve GERD symptoms.
Avoid Late Meals: It is essential to remember that having dinner at least two hours before bedtime allows for proper digestion.
Medications: There are some medications that can help reduce stomach acid production.
GERD is a treatable condition with proper management and appropriate medical care. If you experience symptoms or suspect you may be suffering from complications of this disease, remember that it is always important to seek the attention of a specialist who can provide timely diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan.
At Formé Medical Center, we have a team of specialized professionals who can assist you whether you have mild or severe symptoms. Feel free to call us at 9147234900 or schedule your appointment.